
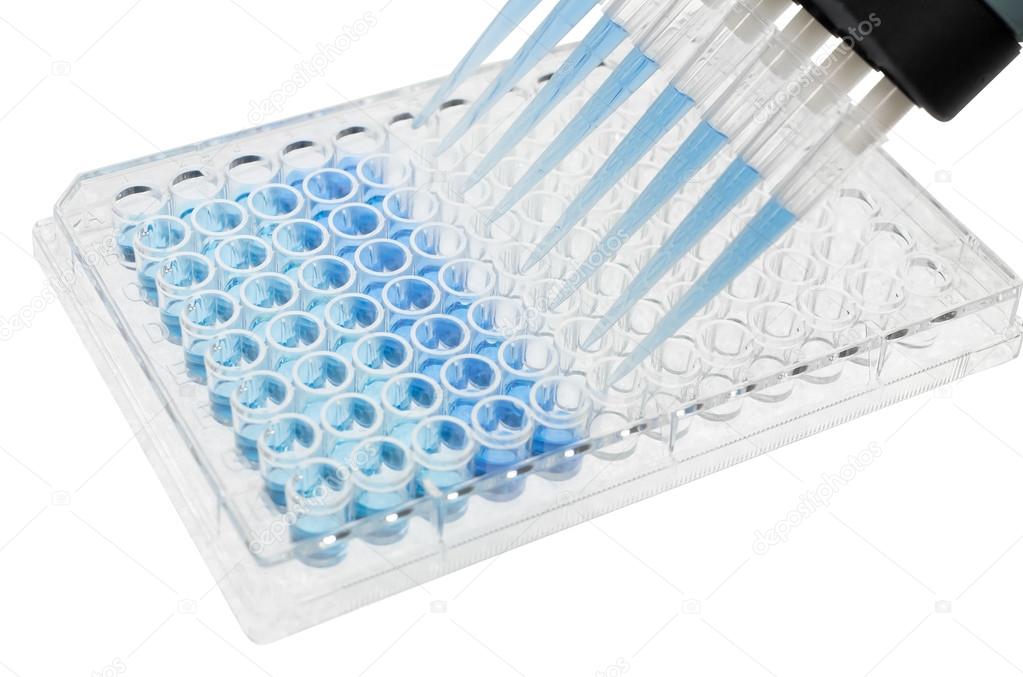
ELISA tests are rapid and easy to carry out, and because they are premeditated to swiftly carry out high throughput screening and multiplexing, they have made a breakthrough in the widespread assessment of various investigations as well as diagnostic assays.ĮLISA has retained its position as widely used detection technique either in their original form or in extended forms with certain amendments i.e. Detection of viruses (HIV, West Nile Virus, and New Castle Disease Virus)ĮLISA has been implemented in diagnostics as well as for quality-control programmes throughout a number of industries.The ability to wash away non-specific unbound reactants makes the ELISA technique an influential and reliable means for gauging precise information on the analytes even when present within a crude and impurified sample. An extremely specific antibody-antigen interaction is the utmost critical component of the entire process. The colored product exhibits absorption at a specific wavelength and can be correlated to the quantity of analyte in question present in the sample. Generally, the ELISA technique results in a colored end product. The detection of the assay is carried out by evaluating the enzyme activity of the conjugate which is implemented by incubation with a suitable substrate for the enzyme resulting in a generation of a quantifiable product. To know more about running ELISA assays, Jump to the protocols page. Therefore, these assays are grouped as ELISAs. Technically, newer assays use reporters that are not enzymes, nonetheless the underlying principles of the assays are similar. The advantage of using advanced reporters help in measuring multiple analytes in a single or cycle of assays (Multiplexing) and higher sensitivities (specificity and sensitivity). Newer Assay techniques make use of fluorogenic, electrochemiluminescent, and quantitative PCR reporters to create quantifiable signals. The conventional ELISA involves usage of chromogenic reporters and substrates to produce color changes to indicate the presence of specific antigen or an analyte. The sensitivity and precision of the assay is enhanced by coating the plate with high-affinity antibodies. The assay combines the specificity of antibody and sensitivity of assay enzymes to primarily detect antigens through assay antibody or antibodies through assay antigens. As radioimmunoassay posed significant health risks to researchers, alternatives were sought.ĮLISA works by coupling antibody or antigen to assay enzyme. Radioactivity served as the reporter signal indicating specific antigen or antibody. In the same period, immunosorbent preparation technique was published by Wide and Jerker Porath.įollowing which, scientists in Sweden (Peter Perlmann and Eva Engvall at Stockholm University) and Netherland (Anton Schuurs and Bauke van Weemen) generated knowledge that go into making ELISAs.īefore ELISA, radioimmunoassay employing radioactively labelled antigens and antibodies were used. Pierce in 1960s laid the ground work for enzyme linking process. This method is rapid, accurate, reproducible, and may be useful for pharmacokinetic and pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic studies as well as in therapeutic drug monitoring of bevacizumab.Two different teams led by Stratis Avrameas and G. Median (range) trough and peak concentrations during the treatment were 47.2 (9.6-106.9) mg/L and 159.3 (33.0-327.3) mg/L, respectively. A total of 175 blood samples was available for analysis from 16 patients. Lower and upper limits of quantitation were 5 and 75 mg/L, respectively. Imprecision and accuracy of calibrators and quality controls were 20% or less, except for the zero calibrator. Bevacizumab concentrations were described using a two-compartment population pharmacokinetic model with first-order constants. Trough and peak serum concentrations of bevacizumab were measured in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Eight calibrators and three quality controls, with concentrations of 5 mg/L, 30 mg/L, and 75 mg/L, were tested on five occasions initially and on five subsequent occasions. Lower and upper limits of quantitation as well as limit of detection were determined. Therefore, an assay to measure bevacizumab serum concentrations is needed.Īn enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was developed using microtiter plates sensitised with vascular endothelial growth factor 165, a recombinant form of vascular endothelial growth factor. It displays an important interindividual pharmacokinetic variability, which could explain part of the interindividual differences in clinical response. Bevacizumab is an antivascular endothelial growth factor humanized monoclonal antibody used to inhibit angiogenesis in cancer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
